Cardiac muscle shares important characteristics with both skeletal and smooth muscle. The cytoplasm of a muscle cells is referred to as sarcoplasm.the plasma membrane is called the sarcolemma and the endoplasmic reticulum is called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.a muscle fiber may also be referred to as a myofiber. Placed end to end, these sarcomeres form long bands called myofibrils. Within a skeletal muscle cell, the numerous myofibrils are separated by glycogen, mitochondria, and muscle triads (two. However, it has inherent mechanisms to initiate continuous contraction like smooth muscle.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/histology-of-skeletal-muscle/CCA8JH8f29ZhIfXBU6FQ_09gjtxSIpcGC6ni5oqNdg_Striations.png)
However, it has inherent mechanisms to initiate continuous contraction like smooth muscle.
They constitute the muscle spindle, and are innervated by both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) fibers. In all types of muscle, contraction is caused by the movement of myosin filaments along actin filaments. Intrafusal muscle fibers are not to be confused with extrafusal muscle fibers, which contract, generating. What is a muscle fiber? 09.05.2021 · skeletal muscle contraction begins first at the neuromuscular junction, which is the synapse between a motoneuron and a muscle fiber. Know what exactly is a muscle cell and what's the difference between a muscle fiber and a muscle fibril. Inward ca2+ flow causes the release of acetylcholine (ach) at the … , collagen, elastic, and reticular), a muscle fiber is actually a single muscle cell ( i.e. Within a skeletal muscle cell, the numerous myofibrils are separated by glycogen, mitochondria, and muscle triads (two. However, it has inherent mechanisms to initiate continuous contraction like smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is broadly classified into two fiber types: They detect the amount and rate of change in length of a muscle. Recent studies have begun to.
Unlike extracellular connective tissue fibers ( i.e. In all types of muscle, contraction is caused by the movement of myosin filaments along actin filaments. Inward ca2+ flow causes the release of acetylcholine (ach) at the … What is a muscle fiber? Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands.

Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands.
Skeletal muscle is broadly classified into two fiber types: Skeletal muscle in cross section and longitudinal section. What is a muscle fiber? Within a skeletal muscle cell, the numerous myofibrils are separated by glycogen, mitochondria, and muscle triads (two. , collagen, elastic, and reticular), a muscle fiber is actually a single muscle cell ( i.e. Know what exactly is a muscle cell and what's the difference between a muscle fiber and a muscle fibril. However, it has inherent mechanisms to initiate continuous contraction like smooth muscle. Intrafusal muscle fibers are skeletal muscle fibers that serve as specialized sensory organs (proprioceptors). Unlike extracellular connective tissue fibers ( i.e. 04.10.2021 · special terms are used to describe structures associated with skeletal muscle tissue. The basic units of muscle are the contractile proteins actin and myosin arranged in sarcomeres. Intrafusal muscle fibers are not to be confused with extrafusal muscle fibers, which contract, generating. Cardiac muscle shares important characteristics with both skeletal and smooth muscle.
Within a skeletal muscle cell, the numerous myofibrils are separated by glycogen, mitochondria, and muscle triads (two. The rate and force of contraction is not subject to voluntary control, but is influenced by the autonomic nervous system and hormones. The basic units of muscle are the contractile proteins actin and myosin arranged in sarcomeres. Skeletal muscle in cross section and longitudinal section. Intrafusal muscle fibers are not to be confused with extrafusal muscle fibers, which contract, generating.
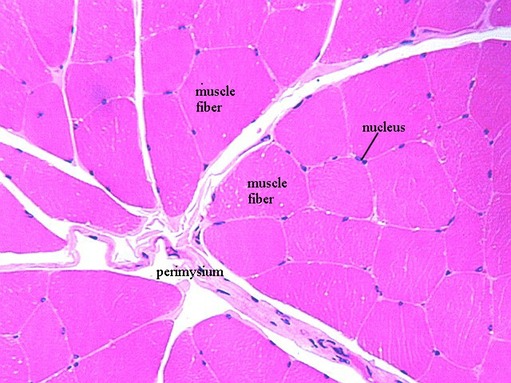
Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands.
Unlike extracellular connective tissue fibers ( i.e. Skeletal muscle is broadly classified into two fiber types: The repeating arrangement of their basic contractile unit, the sarcomere, produces these striations. Functionally, cardiac muscle produces strong contractions like skeletal muscle. 09.05.2021 · skeletal muscle contraction begins first at the neuromuscular junction, which is the synapse between a motoneuron and a muscle fiber. Within a skeletal muscle cell, the numerous myofibrils are separated by glycogen, mitochondria, and muscle triads (two. What is a muscle fiber? Placed end to end, these sarcomeres form long bands called myofibrils. In all types of muscle, contraction is caused by the movement of myosin filaments along actin filaments. Cardiac muscle shares important characteristics with both skeletal and smooth muscle. Know what exactly is a muscle cell and what's the difference between a muscle fiber and a muscle fibril. These findings suggest that some muscle diseases may be treated by shifting fiber type characteristics either from slow to fast, or fast to slow phenotypes, depending on the disease. They constitute the muscle spindle, and are innervated by both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) fibers.
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Histology - Histological Analysis Of Fiber Type And Capillarity In The Download Scientific Diagram -. They detect the amount and rate of change in length of a muscle. Skeletal muscle is broadly classified into two fiber types: Know what exactly is a muscle cell and what's the difference between a muscle fiber and a muscle fibril. The basic units of muscle are the contractile proteins actin and myosin arranged in sarcomeres. What is a muscle fiber?

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar